Same Tree
Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Problem Statement
LeetCode-100: Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not. Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
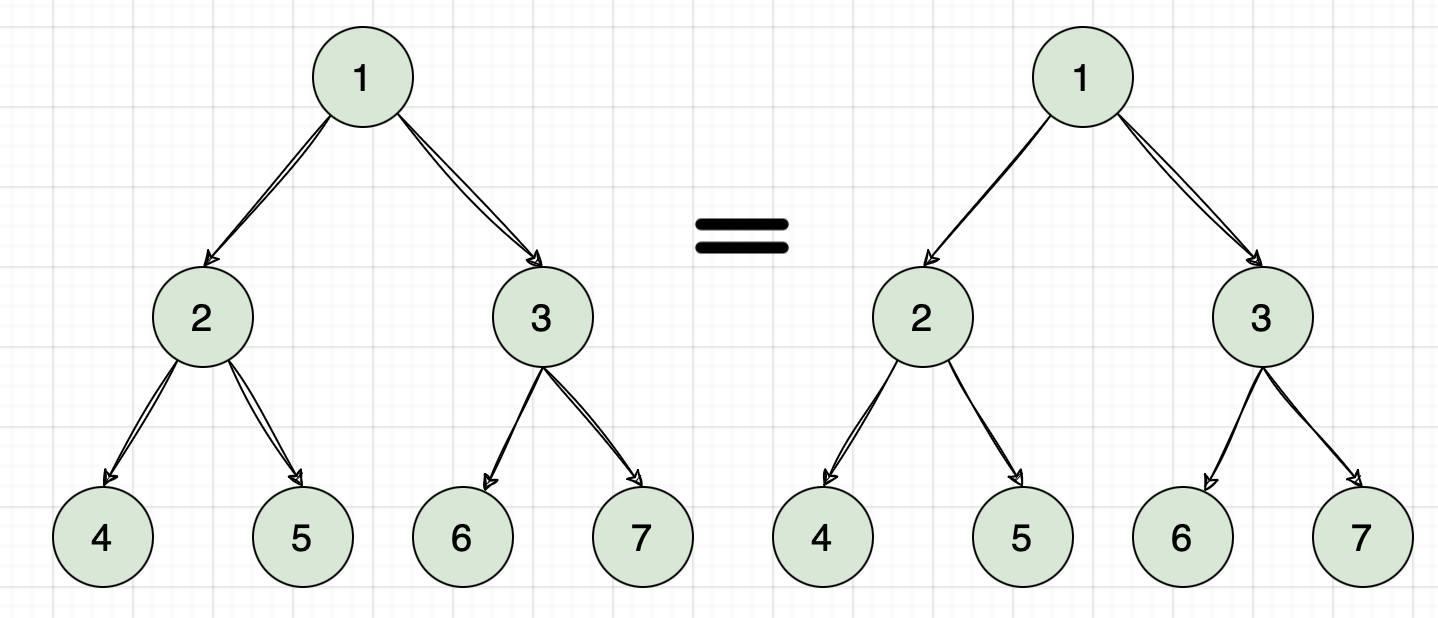
Same Tree
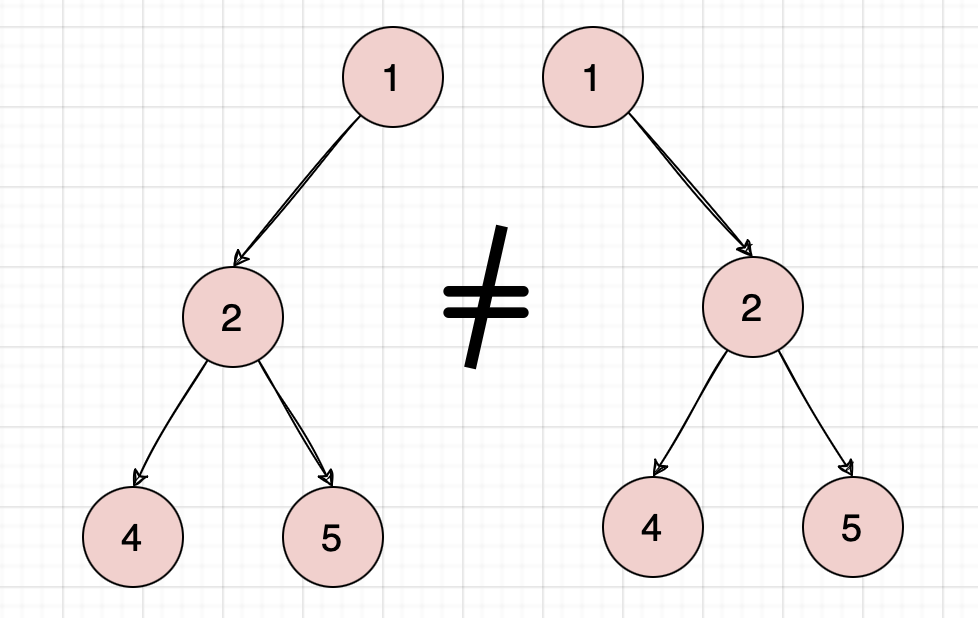
Same Tree
Approach
A clear candidate for a recursive solution. We can check if the current nodes are equal and then recursively check the left and right subtrees.
Base Case: If either of the nodes is null, then both the nodes should be null.
Recursive Case: Check for the following conditions:
- The values of the current nodes are equal.
- Recursively check the left subtree.
- Recursively check the right subtree.
We can also implement an iterative solution (based on level order traversal) using a queue. We can push the nodes of both the trees onto a queue and then pop them one by one and check if they are equal. If they are equal, we can push their children onto the queue.
Implementation
Here is a java implementation of the above approach:
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if(null == p || null == q){
return null == p && null == q;
}
return p.val == q.val &&
isSameTree(p.left, q.left) &&
isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
}
And here is the iterative implementation as discussed above using a queue:
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(p);
queue.add(q);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode pNode = queue.poll();
TreeNode qNode = queue.poll();
// If both nodes are null (probably the children of a leaf node), continue
// If only one of the nodes is null, return false
if (pNode == null || qNode == null) {
if (pNode == null && qNode == null) {
continue;
} else {
return false;
}
}
// If the values of the nodes are not equal, return false
if (pNode.val != qNode.val) {
return false;
}
// Push the children of the nodes onto the queue
queue.add(pNode.left);
queue.add(qNode.left);
queue.add(pNode.right);
queue.add(qNode.right);
}
return true;
}
Complexity Analysis
The time complexity for this approach is $O(N)$ where $N$ is the number of nodes in the tree. The space complexity is $O(H)$ where $H$ is the height of the tree.
The iterative approach has the same time and space complexity as the recursive approach.