Sort Colors
Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
Problem Statement
LeetCode-75: Given an array nums with n objects colored red, white, or blue, sort them in-place so that objects of the same color are adjacent, with the colors in the order red, white, and blue.
We will use the integers 0, 1, and 2 to represent the color red, white, and blue, respectively. You must solve this problem without using the library’s sort function.
Approach
The simplest approach to solve this problem is to count the number of 0, 1, and 2 in the array and then fill the array with the count of 0, 1, and 2 respectively. This approach will take $O(n)$ time and $O(1)$ space.
Here is a Java implementation of the above approach:
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int start = 0;
Map<Integer, Long> freqMap = Arrays.stream(nums)
.boxed()
.collect(Collectors.groupingBy(e -> e, Collectors.counting()));
for (int i = 0; i <= 2; i++) {
// fill the array with the count of i
// use a default value of 0 if the key is not present in the map
int end = start + freqMap.getOrDefault(i, 0L).intValue();
int value = i;
IntStream.range(start, end).forEach(index -> nums[index] = value);
start = end;
}
}
The above approach is not optimal as it requires two passes over the array. We can solve this problem in a single pass using the two-pointer approach known as the Dutch National Flag problem given by Edsger W. Dijkstra.
The approach is based on the following observations:
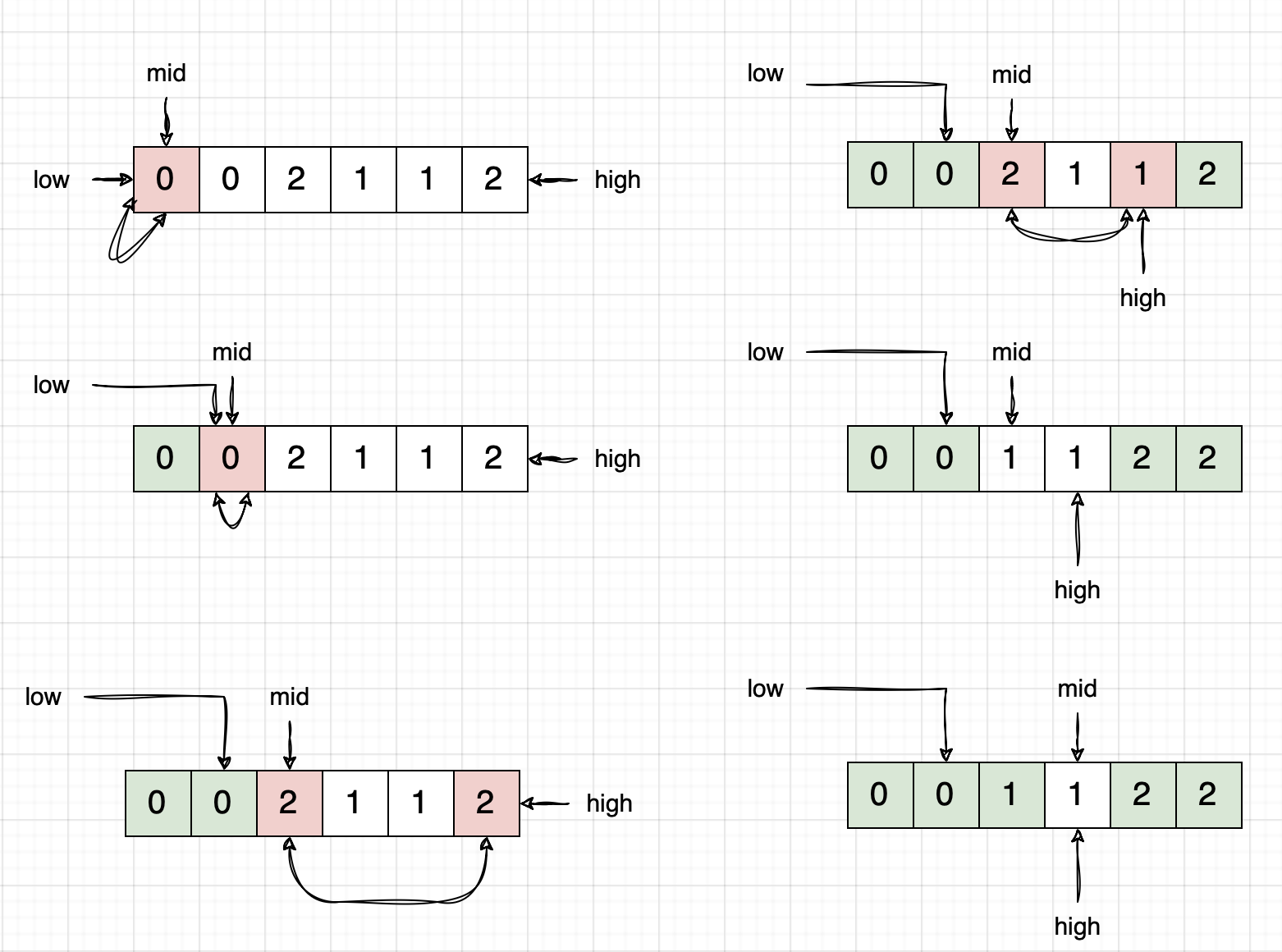
- The array is divided into 4 regions:
0,1,2andunknown.- The
0region is from0tolow-1i.e. all the elements from index0tolow-1should be0. - The
1region is fromlowtomid-1i.e. all the elements from indexlowtomid-1should be1. - The
2region is fromhigh+1ton-1i.e. all the elements from indexhigh+1ton-1should be2. - The
unknownregion is frommidtohighi.e. all the elements from indexmidtohighare yet to be processed.
- The
- Initially all three regions are empty and the goal is to move elements from unknown to the appropriate region.
On a high level, this is done by the following steps:
- Initialize three pointers
low,mid, andhighto0,0, andn-1respectively. - Iterate over the array until
midis less than or equal tohigh. - If the element at
midis0, swap the element atlowandmidand increment bothlowandmid. - If the element at
midis1, incrementmid. - If the element at
midis2, swap the element atmidandhighand decrementhigh. - Continue this process until
midis less than or equal tohigh. - At the end of the iteration, the array will be sorted.
Sort Colors
Implementation
Here is the a implementation of the above approach:
public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
int low = 0, mid = 0, high = nums.length -1;
while(mid <= high){
// if nums[mid] is 0, swap nums[low] and nums[mid] and increment low and mid
// i.e. populate the 0 region
if(nums[mid] == 0){
int temp = nums[low];
nums[low] = nums[mid];
nums[mid] = temp;
mid++;
low++;
}
// if nums[mid] is 2, swap nums[high] and nums[mid] and decrement high
// i.e. populate the 2 region
else if(nums[mid] == 2){
int temp = nums[high];
nums[high] = nums[mid];
nums[mid] = temp;
high--;
}
// if nums[mid] is 1, increment mid
// i.e. populate the 1 region
else{
mid++;
}
}
}
Complexity Analysis
The time complexity of the above approach is $O(n)$ as we are iterating over the array only once. The space complexity is $O(1)$ as we are not using any extra space.